Urinary Tract Infection Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are becoming increasingly common these days. Women are up to 30 times more likely to experience these infections than men, mainly because the urinary system and the end alimentary tract are close enough, making it more susceptible to bacteria. This problem typically occurs when a different type of bacteria makes its way into the tract from an unintended source. In this blog, Dr. Jyoti Mohan Tosh, a urologist in Bhubaneswar (CARE Hospital), sheds light on why women are more prone to UTIs than men and shares more insights on the subject. So, what exactly is a urinary tract infection? A urinary tract infection happens when fecal bacteria reach the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the bladder. Bacteria can also enter the urethra through sexual contact, leading to this medical condition.UTIs can be categorized into three main types:1. Urethritis, which is the inflammation of the urethra. 2. Cystitis, which occurs when the infection spreads from the urethra to the bladder. While these are the most common and easily treatable infections, there’s a risk of the infection moving from the bladder to the kidneys.3. Pyelonephritis, a more serious and less common kidney infection. What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection? A urinary tract infection can lead to several symptoms, including:– A strong and persistent urge to urinate– A burning sensation during urination– Frequent urination in small amounts– Cloudy urine, or urine that appears red, pink, or brownish– Foul-smelling urine– For women, pelvic pain, especially in the center of the pelvis and around the pubic bone.If you’re seeking effective treatment for a urinary tract infection in Bhubaneswar, consider reaching out to urologist Dr. Jyoti Mohan Tosh. With extensive experience in addressing all kinds of urological issues and infections, he can provide the effective care you need.Here are the top 7 reasons why women tend to get more UTIs than men.1. Anatomical structureA urinary tract infection (UTI) happens when Escherichia coli bacteria from the outer genitals and the area around the anus make their way into the urinary tract and reach the bladder. Since E. coli bacteria are naturally present in these areas, women are at a higher risk. The urethra, which carries urine from the bladder, is relatively short, allowing bacteria to enter the urinary system quickly. This contamination of the perineum and urethral regions is often the main culprit behind urinary infections in women.2. Sexual activitiesMany women find themselves dealing with cystitis after becoming sexually active or starting a relationship with a new partner. This is because intercourse can introduce different strains of bacteria into the vaginal and urethral areas. Additionally, if women don’t urinate right after sex, bacteria can linger in the urinary tract, multiplying and leading to an infection.Being mindful of proper hygiene, especially during sexual activity, can help women steer clear of UTIs. Simple habits like urinating after intercourse and keeping the area clean can significantly reduce the risk of infection.3. Use of birth control methodsCertain birth control methods, like spermicidal agents and diaphragms, can increase a woman’s chances of developing bladder infections. Many spermicides contain chemicals that are linked to a higher risk of urinary infections. Meanwhile, diaphragms can irritate the areas around the bladder, making it easier for bacteria to latch onto the inner linings.4. GeneticsThere’s some evidence suggesting that genetics may play a role in making women more prone to UTIs. A close look at family history can often reveal patterns of recurrent bladder infections among relatives. This could be due to a higher density of specific carbohydrate receptors that certain strains of E. coli can attach to.Unfortunately, if a woman suspects that her urinary infections are hereditary, there’s not much she can do about it. It’s essential to seek medical attention promptly to help manage the situation and reduce severity.5. MenopauseAs women age, they become more vulnerable to urinary tract infections (UTIs). Bacteria in the urine, often referred to as bacteriuria, affects about 10% to 15% of women between the ages of 65 and 70, and this number jumps to 20% to 50% for women aged 80 and older. If a woman has had a bladder infection, like cystitis or kidney issues, before menopause, she’s likely to experience recurring infections during menopause and after. Several factors could contribute to this, including genetics, hormonal changes, and other age-related health issues.6. More sensitive skinThe external urethral meatus in women is made up of mucosa, the moist tissue that lines the vagina. Compared to men, this skin is thinner and more delicate than most other skin on the body. Because of this, the female urethra is more prone to damage and inflammation. When the skin becomes inflamed, it creates a welcoming environment for bacteria, which can easily travel up the short distance to the bladder.7. PregnancyPregnant women are also at a higher risk for UTIs. Serious infections can pose risks to both the mother and her baby. If a woman suspects she has a UTI, it’s crucial to reach out to her obstetrician right away to get the necessary treatment as soon as possible.Prevention Tips:Despite maintaining good hygiene, women are generally more susceptible to urinary tract infections than men. However, there are some hygiene practices that can help reduce the risk of UTIs. Most people know that wiping from back to front after urinating can lead to a UTI due to bacteria like E. coli. But it’s worth noting that wiping from front to back can also spread bacteria. Instead, consider using the blotting technique. Gently blot the urethra or the upper part of the vagina with clean, folded toilet paper (preferably undyed and unscented). Blotting, rather than wiping, helps keep bacteria away from the urethra. Baths have also been linked to UTIs. While dirty bathwater can certainly lead to infections, there are ways to enjoy a soak without worry. If a woman loves to relax in the tub, she can take precautions to minimize the risk.When it comes to treating urinary tract infections (UTIs)
What is BPH? A Complete Guide to Enlarged Prostate
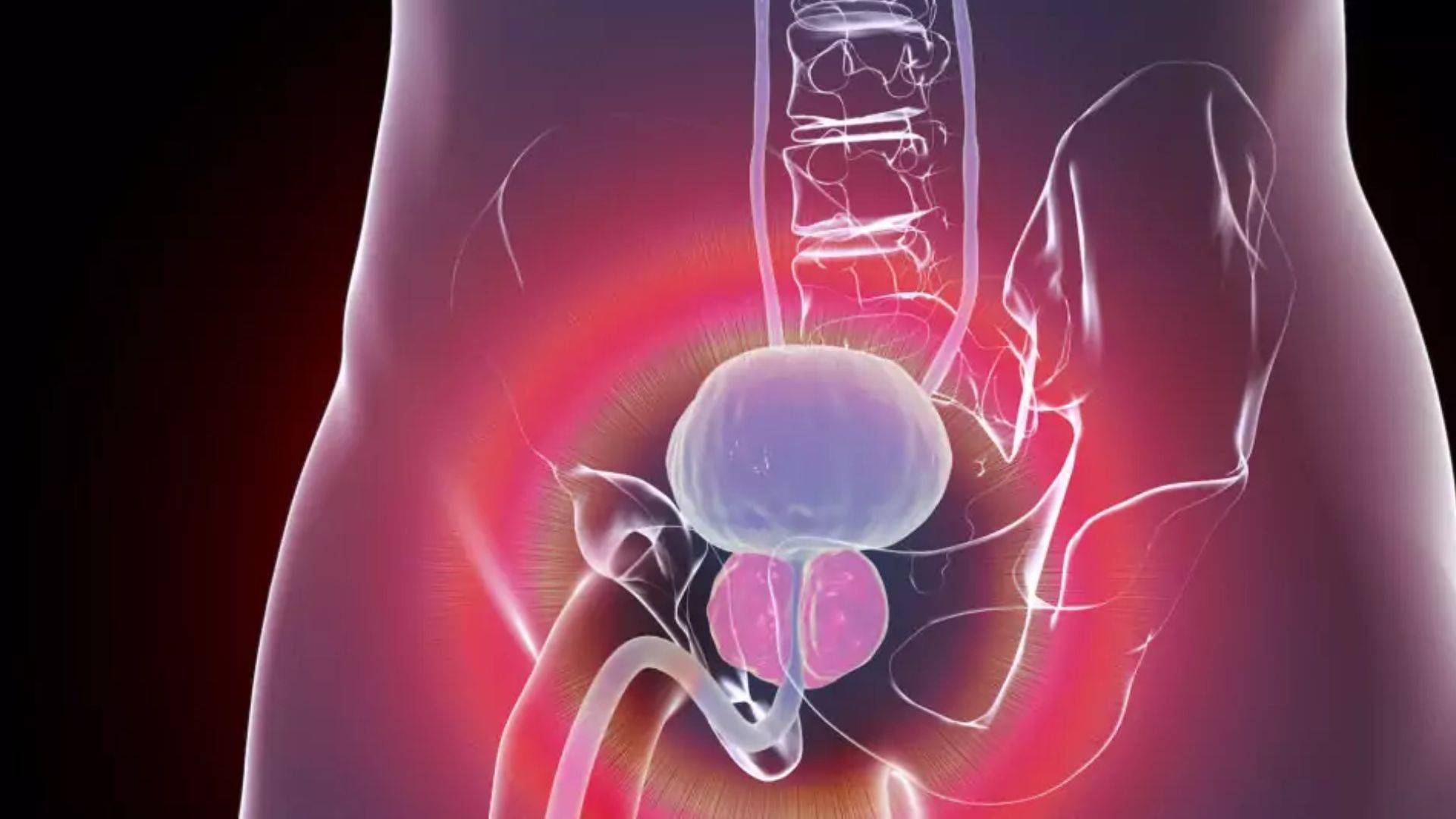
What is BPH? A Complete Guide to Enlarged Prostate Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that affects millions of men, particularly as they age. Though not life-threatening, BPH can significantly impact a man’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can help individuals make informed decisions about their health. What is the Prostate Gland? The prostate is a small, walnut-shaped gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. The prostate plays a critical role in male reproductive health, producing a fluid that forms part of semen.As men age, the prostate naturally grows larger. While this growth is normal, excessive enlargement can lead to BPH, causing urinary problems due to the gland’s pressure on the urethra. Causes and Risk Factors of BPH 1. Causes: The exact cause of BPH is not entirely understood, but it is associated with hormonal changes that occur with age. Testosterone, the primary male hormone, decreases over time, while estrogen levels remain relatively stable. This hormonal imbalance may contribute to prostate growth. Additionally, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, accumulates in the prostate, stimulating cell growth.2. Risk Factors: Several factors increase the likelihood of developing BPH:* Age: BPH is rare in men under 40 but becomes increasingly common after 50, affecting nearly 50% of men by age 60 and up to 90% by age 85.* Family History: A genetic predisposition to BPH can increase risk.* Lifestyle: Obesity, lack of exercise, and a poor diet may contribute to the condition.* Chronic Health Conditions: Diabetes and heart disease are linked to a higher incidence of BPH.3. Symptoms of BPHBPH symptoms are primarily urinary and fall under two categories:Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)a. Obstructive Symptoms: Difficulty starting urination, weak urine flow, intermittent flow, or the sensation of incomplete bladder emptying.b. Irritative Symptoms: Frequent urination, urgency, nocturia (waking up to urinate at night), and in some cases, urinary incontinence. Complications Untreated BPH can lead to complications such as urinary retention, bladder stones, recurring urinary tract infections (UTIs), or kidney damage. DIAGNOSIS of BPH Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:1. Medical History: The doctor will ask about urinary symptoms, lifestyle, and family history of prostate issues.2. Physical Exam: A digital rectal exam (DRE) is performed to assess the size and texture of the prostate.3. Urinalysis: This test checks for blood, infection, or other abnormalities in the urine.4. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: PSA levels can be elevated in BPH but are also linked to prostate cancer.5. Uroflowmetry: These assess average , maximum flow, voided volume, and many other flow parameters.6. Imaging Tests: Ultrasound may be used to evaluate the prostate and urinary tract.7. Cystoscopy: A small camera is inserted through the urethra to examine the bladder and prostate. TREATEMENT OPTIONS FOR BPH Treatment for BPH depends on the severity of symptoms, the size of the prostate, and the individual’s overall health.Lifestyle Changes* Reduce fluid intake before bedtime or social outings.* Limit caffeine and alcohol, as they can irritate the bladder.* Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly.* Avoid medications that worsen symptoms, such as decongestants.Medications* Alpha Blockers: Relax prostate and bladder neck muscles to improve urine flow. Examples include tamsulosin and alfuzosin.* 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: Reduce prostate size by inhibiting DHT production. Examples include finasteride and dutasteride.* Combination Therapy: Using both alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors for better results.Other Medications: Anticholinergics or beta-3 agonists may be prescribed for irritative symptoms.Minimally Invasive ProceduresFor moderate to severe cases, minimally invasive options include:* Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): Removes prostate tissue to ease urinary flow.* Transurethral Microwave Therapy (TUMT): Uses heat to reduce prostate size.* Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL): Inserts implants to keep the urethra open.* Water Vapor Therapy: Steam is used to destroy excess prostate tissue.SurgerySurgical options are reserved for severe cases or when other treatments fail:* Open Prostatectomy: Removes part or all of the prostate.* Laser Surgery: Vaporizes or cuts away prostate tissue with minimal bleeding and faster recovery.Managing Life with BPH Living with BPH requires ongoing management:Regular Monitoring: Frequent check-ups to assess symptoms and prostate size.Symptom Tracking: Keeping a diary of urinary habits can help identify triggers and improvements.Support Groups: Joining a community can provide emotional support and practical advice.Prevention of BPH While BPH cannot always be prevented, certain habits can reduce the risk:* Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.* Stay active to maintain a healthy weight.* Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.* Manage chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension effectively.When to See a Doctor Men experiencing urinary difficulties should seek medical advice, especially if symptoms interfere with daily life or if complications like urinary retention arise. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and improve outcomes.CONCLUSION Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is a common condition that can significantly affect urinary health and overall quality of life. Understanding the risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and exploring treatment options are essential for effective management. With advancements in medical care and lifestyle modifications, many men can lead a healthy and comfortable life despite a BPH diagnosis. If you suspect you have BPH or are experiencing related symptoms, consult a healthcare provider to create a tailored treatment plan.If you’re experiencing symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) or have concerns about your urinary health, don’t wait to seek expert care. Dr. Jyoti Mohan Tosh, a highly experienced urologist, specializes in diagnosing and treating BPH with personalized, compassionate care.Take the first step toward relief and improved quality of life. Schedule your consultation with Dr.Jyoti Mohan Tosh today!Your health and comfort are our priority—let us help you regain control.
Erectile dysfunction – A guide
WHAT IS ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION? Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It can result from multiple factors like decrease in blood flow, weak pelvic floor muscles, multiple cormorbidites, or unhealthy life style habits. It not hampers your sexual life but increases mental stress and creates a social stigma. If you are suffering from this problem don’t hesistate to visit your urologist. everything can be treated if you treat at right time. WHAT CAUSES AN ERECTION? An erection occurs when blood flows into the penis, causing it to become firm and engorged. This process is primarily controlled by a combination of physical and psychological factors. Here’s a breakdown of what causes an erection:1. Sexual Arousal: The brain sends signals through the nervous system to the penis when the person is sexually aroused either by physical touch, visual stimuli, thoughts, or emotions2. Nerve Response: The brain’s signals travel down the spinal cord and nerves to the penis. This stimulates the release of chemicals like nitric oxide, which relaxes penile blood vessels.3. Blood Flow: Increased blood flow to erectile tissues (corpora cavernosa) inside the penis makes it erect.4. Pressure Build-Up: As blood fills the erectile tissues, it becomes trapped, which increases girth and length of penis.In summary, an erection is the result of a complex interaction between the brain, nervous system, blood vessels, hormones, and psychological factors. If any path is affected its causes erectile dysfunction. CAUSES OF ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION: 1. Physical Causes:Cardiovascular diseases (e.g., heart disease, high blood pressure)Diabetes Obesity Hormonal imbalances (low testosterone levels)Neurological disordersPeyronie’s disease 2. Psychological Causes:Stress Anxiety DepressionRelationship problems 3. Lifestyle Factors:Smoking Excessive alcohol consumptionLack of physical activity Unhealthy diet 4. Medications and Treatments:Certain medications (e.g., for high blood pressure, depression, or anxiety)Treatment side effects (e.g., chemotherapy or surgery) 5. Age-Related Changes:Natural decline in testosterone levels Decreased blood flow and nerve sensitivity Erectile dysfunction can often be caused by a combination of these factors. Consulting a healthcare provider can help identify the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. HOW CAN I PREVENT ED Preventing erectile dysfunction (ED) involves making lifestyle changes and taking steps to maintain overall health. Here are some key ways to reduce the risk:1. Maintain a Healthy Diet:Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.Avoid excessive consumption of processed foods, unhealthy fats, and sugary snacks. 2. Exercise Regularly:3. Manage Stress and Mental Health:4. Maintain a Healthy Weight:5. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption:6. Get Enough Sleep:Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep can affect hormone levels, including testosterone, which plays a key role in sexual function.7. Monitor Your Health:Regularly check and manage conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol. Keeping these in check can prevent ED.Have routine check-ups with your doctor to monitor your heart health, blood sugar, and hormone levels.8. Avoid Drug or Substance Abuse:9. Stay Engaged in a Healthy Relationship: By adopting these lifestyle habits and taking proactive measures, you can reduce your risk of erectile dysfunction and improve overall well-being. If you have concerns about your sexual health, it’s always a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider for personalized advice. WHAT IS TREATMENT IN ED There are various treatment options available for erectile dysfunction (ED), depending on the underlying cause. Here’s a comprehensive list of treatment options:1. Oral MedicationsPDE5 Inhibitors (Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors): These medications help relax the muscles in the penis and increase blood flow. Common options include:Sildenafil (Viagra)Tadalafil (Cialis)Vardenafil (Levitra)Avanafil (Stendra)2. Hormonal TreatmentsTestosterone Replacement Therapy: (via injections, patches, gels, or pellets)3. Psychological CounselingTherapy or Counseling: psychologist or counselor may be effective in relieving stress and anxiety. This may include:Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)Couples Therapy4. Vacuum Erection Devices (VED)A vacuum pump is a non-invasive device that creates a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into it and causing an erection. A constriction band is then placed at the base of the penis to maintain the erection.5. Penile InjectionsIntracavernosal Injections: Medications like alprostadil are injected directly into the penis to enhance blood flow and cause an erection. Other medications used in injections may include papaverine or phentolamine.6. PRP Therapy: They involve using stem cells or plasma from the patient’s blood to stimulate tissue growth and improve blood flow to the penis.7. Urethral SuppositoriesIntraurethral Therapy: A small pellet of alprostadil can be inserted into the urethra using an applicator.8. Penile Implants (Surgical Options) Penile Prosthesis: A surgical option for those with severe ED or when other treatments have not worked. There are two main types:a. Inflatable implants: A pump inserted into the scrotum is used to inflate the implant, providing an erection.b. Malleable implants: These are semi-rigid rods that are placed in the penis and can be manually adjusted.9. Shockwave TherapyLow-Intensity Shockwave Therapy: This treatment uses sound waves to stimulate blood flow and promote tissue regeneration in the penis. It may be used as a non-invasive option for men with ED, especially in cases where other treatments are not effective.10. Vascular SurgeryArterial Surgery: In rare cases, when ED is caused by blocked or narrowed arteries (such as in younger men), surgical procedures can help improve blood flow to the penis.Venous Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be done to prevent blood from leaking out of the penis during an erection.11. Alternative TreatmentsHerbal Supplements: Some people may turn to herbal remedies like ginseng, yohimbine, or L-arginine. However, these are not scientifically proven and can have side effects or interactions with other medications.Acupuncture: Some studies suggest acupuncture may help relieve stress-related ED, though it’s not widely recognized as a primary treatment.Choosing the Right Treatment: The best treatment option for ED depends on the underlying cause, severity, and individual preferences. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider to discuss options, especially if the ED is linked to underlying health conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or hormonal imbalances. The healthcare provider can recommend the most appropriate treatment based on the individual’s specific needs. If you’re experiencing symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction or have